These days, automation is the talk of the town – and the food industry is no exception. Research and Markets predict that the global food automation market is poised to reach $14 billion by 2025.
With each passing day, companies are developing, improving, and perfecting impressive technology to automate daily processes. This in turn brings promises of lower operational costs, more efficient customer service, and an overall boost in productivity.
But a lot of this technology is still in the early stages of acceptance, and there's a lot of growth and specialization that needs to happen before the robots can take over food service as we know it.
Let's discuss the state of automation in the restaurant industry, as well as some benefits and challenges presented by it.%20(1).webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(6)%20(1).webp)
What is restaurant automation?
The use of technology to facilitate various types of operations within a hospitality business is known as restaurant automation. This can range from using robotics in the back office to using point-of-sale software to automate tasks such as customer orders and inventory.
From disruptions in the supply chain to labor issues, restaurants' business models have shifted dramatically. Labor shortages are one of the industry's most pressing issues right now, with full-service restaurants employing 6.2 fewer kitchen employees than in previous years.
Many restaurants have had to rely on automation to keep their operations running due to a lack of staff.
Approximately half of all restaurants in the United States intend to use this type of technology in the coming years to address labor shortage issues.
Not only that but incorporating restaurant technology is regarded as nearly essential for survival, with 87% of industry and restaurant operators all agreeing that technology adoption has been critical throughout the pandemic.
.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(18).webp)
The Advantages of Restaurant Automation
-
Simplifies processes and optimizes operations
-
Lowers operational costs
-
Eliminates user error
-
Lowers waste
-
Works with a small staff
-
Lowers turnaround times
-
Improves customer satisfaction
How automation is impacting restaurants
At its core, restaurant automation makes things more efficient – when done right, it can simultaneously decrease a restaurant's costs while increasing efficiency. And while some of this tech comes with a hefty price tag, new developments and improvements to old ones are making these systems more accessible and affordable.
That's why we can expect that more restaurants will continue to jump on the automation train as the industry continues to mature and specialize.
-1.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(3)-1.webp)
Different kinds of automation tools in the restaurant industry
Restaurant automation tools come in a variety of shapes and sizes to serve various aspects of your hospitality business. There are different types of restaurant automation technology for each need, whether you need extra help in the back of house by automating repetitive tasks or you want to let customers place their own orders when working with limited staff.
Here's a more in-depth look at these innovative tools, divided into automated restaurant equipment found in the front of the house (FOH) and back of the house (BOH).
Automation at the front of the house
Restaurants experiencing labor and staffing shortages can use a variety of tools to help alleviate the workload, such as giving customers more control over their dine-in order taking, freeing up staff to attend to other customers, or assisting in other areas of the restaurant operations.
Among the most popular and easily accessible FOH restaurant automations are a mobile point-of-sale (POS) system, QR code menus, customer-facing displays, self-ordering kiosks, and digital waitlists.
Mobile Point of Sale system that help reduce repetitive tasks
Description: A POS is arguably the most important piece of technology in a restaurant because it serves as the hub for all transactions. This hardware-software combination processes orders and payments generates reports, send orders to the kitchen, and does a plethora of other simple tasks.
How it saves you money: Your POS is a goldmine of information about your company. Reports enable you to make data-driven (rather than gut-based) decisions that can save you money. A POS report, for example, can help you understand when your restaurant is busiest so you can schedule more employees to work during those times and fewer employees when demand is low. You also don't have to manually run orders to the kitchen or enter payment data because your POS syncs with other parts of your restaurant, such as your kitchen display system or payment processor. This connectivity allows employees to spend less time on repetitive tasks like manual data entry.
Digital menus and QR codes
Description: QR code ordering has grown into a standard feature of modern restaurant ordering. Customers can access a digital menu by scanning the QR codes that are often placed on each individual table. Customers can view the menu as soon as they are seated, rather than having to wait for a server to bring them a physical menu. Some restaurants also offer online ordering in conjunction with their digital menu, allowing customers to not only view the menu but also place an order directly from their phones. Customers have more control over their orders with digital menus and online ordering, and it allows staff to focus on the experience rather than just taking orders and bringing order information to the back of house.-1.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(8)-1.webp)
How it saves you money: When your restaurant's menu is available digitally, hosts and servers can also save time by not having to go to each guest's table to deliver menus. This allows staff to spend more time engaging with guests in meaningful ways, such as answering menu questions or making personalized recommendations.
Furthermore, when customers can place and pay for online orders all on their own, servers no longer need to visit their tables to take orders or process payments, allowing you to have fewer staff members on payroll and give them more impactful duties.
Self-service kiosk
Description: Self-ordering kiosks are digital screens that allow customers to place and pay for their own orders without interacting with a staff member. Fast food and fast casual restaurants are the most common users of these kiosks.
How it saves you money: Self-service technology allows you to increase your order-taking capacity without having to hire additional staff to work at your front counter. If you need to cut costs, setting up a kiosk can help you keep your current order capacity while using labor costs and reducing the number of people you need working your FOH. Staff can focus on duties other than taking orders with the help of kiosks, allowing you to run a more efficient operation..webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(12).webp)
A digital waitlist solution
Description: A digital waitlist allows walk-in customers to add themselves to a waitlist and check their position in line using their mobile devices. With software like Eat App, guests can even add themselves to the list remotely before arriving so that their table is ready when they arrive at the restaurant.
How it saves you money: By allowing guests to add their names to the waitlist, hosts can spend less time managing the waitlist and more time interacting with customers, taking reservations, or processing takeout orders. And, because a digital waitlist can show guests when their table will be ready with automated reminders, hosts can relieve themselves of that responsibility.
.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(15).webp)
A customer-facing display screen
Description: A customer-facing display is a digital screen (typically a tablet) that allows diners to view and confirm their orders. This display typically shows the items ordered, their prices, and any modifications requested by the customer. This tool greatly improves the customer experience by allowing guests to see the details of their order, thereby avoiding confusion, mistakes, and delays.
How it saves you money: When a customer can confirm that their order was correctly entered into the POS, staff can avoid wasting time fixing errors. Customer-facing displays also assist employees in bringing out the correct food and beverages the first time, reducing the amount of time they need to spend running back and forth to the kitchen and increasing efficiency.
-1.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(9)-1.webp)
Restaurant back-of-house automation technology
BOH automations can reduce kitchen staff workload and give them more time to focus on the speed and quality of the food being prepared.
Display system for the kitchen
Description: A kitchen display system (KDS) is a digital ticket system used in the kitchen. Orders entered into the POS are automatically displayed on a screen at the appropriate station in the kitchen, allowing staff to know what to prepare and when.
How it saves you money: A kitchen display system eliminates the need for a FOH team member to run physical tickets to the kitchen or to print tickets and then distribute them among kitchen stations. Staff can avoid spending time correcting errors by automatically sending the digital ticket to the correct station. A KDS also saves time for kitchen staff by optimizing course timing, allowing cooks to work much more efficiently during service.-1.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(10)-1.webp)
Inventory management system
Description: Inventory software keeps track of what you have on hand and when it needs to be reordered. Inventory software can also keep your staff informed by sending pop-up alerts when an item is running low.
How it saves you money: Inventory management systems automatically update levels based on what's been requested through the POS, eliminating the need for dedicated staff members to manually count inventory. Some systems will even order new stock for you when you reach your reorder point, taking the entire process off your to-do list.
.webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(11).webp)
Automation of online ordering and delivery
Description: A direct online ordering system allows your restaurant to accept takeout and delivery orders online, as well as process payments for those orders. Direct online ordering systems, as opposed to third-party ordering platforms, which pit your restaurant against the competition and charge high commission fees on each order, are embedded into or linked from your website and do not charge commission fees.
How it saves you money: You can use delivery integrations to automate order management and communication with delivery drivers if you have your own online ordering platform. You can manage orders directly through your automated delivery POS with this type of integration, and delivery drivers are automatically dispatched as soon as you receive an order..webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(14).webp)
The highs and lows of labor and robots

There are numerous perks for restaurants that can find the right balance of human labor and automation.
Leading provider Ziosk states that automation can expedite the dining process by roughly six to nine minutes, as customers don't need to wait on servers to take their orders or fulfill other requests. Faster experiences naturally translate into more customers per day, which means higher revenue for restaurants.
As a bonus, this more efficient experience can also encourage higher tickets: another provider, Buzztime, claims that its self-service POS system boosts customer checks by an average of 21 percent..webp?width=2240&height=1260&name=Women%20At%20Eat%20(19).webp)
When you couple increased efficiency and revenue with fewer wages paid to personnel and less error caused by those workers, you have a clear recipe for a sustainable, lucrative business model.
However, this key benefit doubles as one of the biggest controversies. Around the world, workers are worried that they'll be replaced by robots, with their skills made obsolete.
One story reports that up to one-quarter of U.S. jobs could be replaced by 2030. Going further, this impact on the workforce creates anticipation around its potential impact on local and global economies. While there's no way to predict the outcome, it's certain that the workforce will evolve in response to this new tech.
Next, take a look at two examples of robotic restaurants that are paving the way for others.
Examples of robotic restaurants
Spyce and Zume have paved the way for revolutionary business models for quick-service restaurants that embrace automation. Let's explore these restaurants and their approach.
Spyce
Founded by four robotics engineers from MIT, Boston-based Spyce is the world's first restaurant of its kind. It features a robotic kitchen that cooks each meal fresh to order in three minutes or less.
“Our woks cook by constantly tumbling your food, which provides a really nice and even sear,” says Co-Founder and Lead Mechanical Engineer Luke Schlueter. “They're heated with induction and we have temperature control to perfectly cook your meal every time.”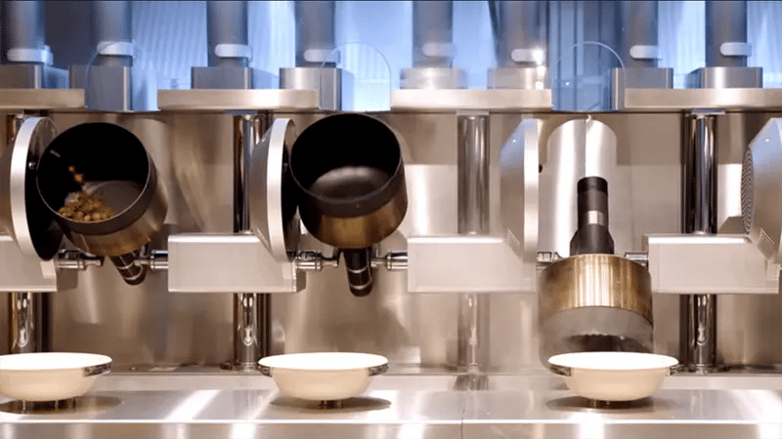
Daniel Boulud, Culinary Director and Michelin-star chef, discusses his first introduction to the concept, saying that a robotic kitchen was something that left him puzzled. He needed to come to Boston.
Skeptical at first, Boulud was soon won over by the new concept, he discovered that the robotic kitchen brings precision, consistency, taste, and freshness to the preparation.
Zume
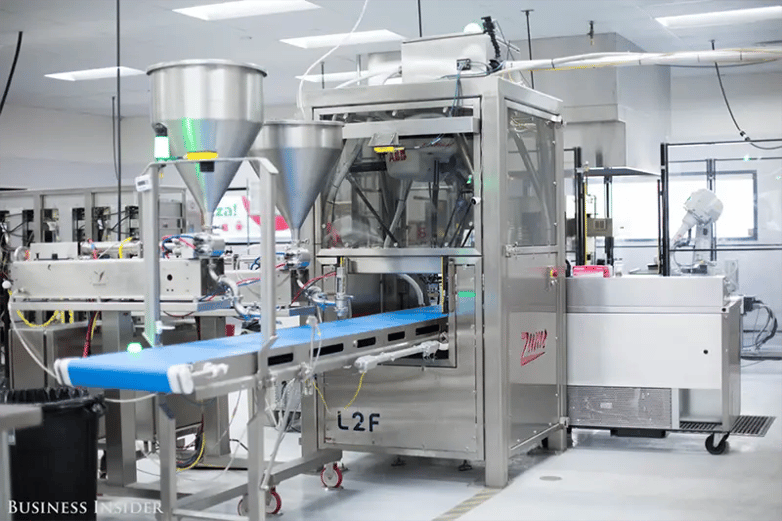
Based in California's Bay Area, Zume Pizza combines human labor and robotics for a new take on a pizza shop. Robots handle repetitive tasks like rolling out dough, adding and spreading sauce, and carrying each pizza into and out of the oven.
It's all done in a fraction of the time it would take human staff, allowing the company's headquarters to pump out up to 370 pizzas an hour.
Zume has recently added a fleet of special delivery trucks, featuring smart ovens that are letting customers cook pizzas on the way to their destinations.
Alex Garden, CEO and Chairman of Zume, believes that robots and artificial intelligence are here to improve life for their human counterparts. “We believe that automation exists to improve human lives – first with our employees, then our community and customers,” he says.
So, for every unit of robotics or automation Zume introduces into its kitchen, they first ask themselves how will this addition improve people's lives? Does it make the environment safer and more fulfilling for their personal? Does it improve the quality of service being provided to their customers?
In November 2018, the company snagged $375 million in investment to grow the enterprise and expand its food tech to more businesses.
What are the benefits of restaurant automation?
Let’s go over some of the key benefits of restaurant automation for the front-of-house and back-of-house.
Front-of-House
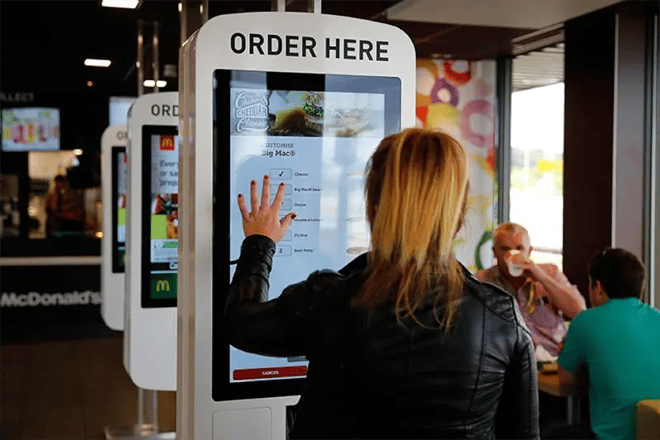
Ordering kiosks. Kiosks are quickly becoming a standard in the fast food industry. Major chains like McDonald’s, Wendy's, and Panera Bread are already testing the waters in some of their locations.
These kiosks allow customers to stroll up, tap their orders in, and complete payment without any assistance from human employees. Results have been promising so far, suggesting that these will soon become more widely adopted by smaller restaurants, too.

Reservations. Restaurant reservations are ripe for disruption from automation - in fact it has already been happening over the past 10 years. Hosts can spend hours per day on the phone taking and confirming reservations. At busy restaurants this can require 2 or 3 full time staff just to manage bookings.
Reservation automation systems, like Eat App, can help restaurants automate the reservation process through online booking systems. In these systems guests can see real-time table availability on the restaurant website and place confirmed directly. These systems can also seat guests automatically and optimize table allocations without the host stand lifting a finger.
Reservation automation is one of the easiest, and cheapest, ways restaurants can get started with automation. Learn more with the video below.
Capacity management. Anyone who’s worked in food service can attest to how stressful it can be when a restaurant meets or exceeds capacity. Employees are stressed, capabilities are stretched, and customers are impatient or possibly unhappy.
A smart system can help ensure this doesn’t happen by keeping track of capacity in real-time. When things get tight, the system can take several elements into consideration to make important judgment calls. This can in turn create smoother experiences for restaurants and their customers during peak hours.
Using a restaurant management software can help manage capacity issues for your restaurant by helping you derive a floor plan and understanding thoroughly about the available capacity at any given time in order to avoid overbooking or underbooking.
Back-of-House
Cooking process. As we saw in the examples of Spyce and Zuma above, robots do an excellent job when it comes to repetitive and dangerous tasks like food prep and activities that involve contact with direct heat.
This can help to expedite cooking, while consistently creating predictable results and helping to foster safer working conditions throughout the entire cooking process.
Inventory management and food waste. One of the downfalls of humans doing the inventory management and cooking is that it’s practically impossible to perfectly predict what you’ll need in the coming period, as well as ensuring that each dish is perfectly portioned.
Robots can help with both of these challenges. Smart tech can use analytics and prediction to measure food use and place intelligent ingredient orders, while automated measuring can ensure that portions are right where they need to be.
Automated Delivery
The automation revolution can also significantly impact the process of delivery for restaurants. Several futuristic technologies are already being used by various food chains for faster, smoother & more efficient food delivery.
For instance, Dominos Pizza is testing a high-tech, autonomous robot, DRU developed by Starship Technologies programmed with inbuilt cameras & GPS systems that carries about 4-5 medium pizzas and delivers them independently to the customers via a code delivered to their phone while can be used to unlock the cargo area to access the pizzas.
Though technology like DRU is currently still in testing phases, it indicates the upcoming wave of change in the way restaurants deliver food driven by automation and technological advancements.
What are the downsides of automation?
While automation can help solve a lot of common foodservice challenges, it's no silver bullet. Here are a few issues that prove that the robot takeover of restaurant chains isn't as close as some may think.
High implementation costs. Cost is a huge barrier to entry for restaurants. Smart and responsive machines can be incredibly expensive to obtain and tweak to ensure they cater to the nuances of your restaurant.
With that said, the tech has the ability to quickly earn back the investment – but only for the companies that can afford the time in between.
Inability to make complex judgment calls. Apart from keeping labor costs down, another big issue is that robots simply can't replace the complex functionality of the human brain. (And the ones that come close are still way too expensive to make sense to many businesses.)
For example, unless they've been specially developed to do so, robots can't tell if an ingredient is going bad or a meal has burned. If a customer requests a certain change to a dish, a robot can't fulfill the request unless it's been programmed.
Lack of human connection. Human connections are one of the pillars of a customer's restaurant experience. From being greeted with a smile to having their needs consistently accommodated, a strong emotional connection can turn a mediocre dining experience into an amazing one.
While robots can certainly make the ordering process faster and less prone to human error, it simply can't replace the connections that happen every day when people come together over a good meal.
People vs. Robots: should the human workforce be worried?
The most critical question that arises with the spurring growth of automation in the restaurant industry is - are these high-tech robots going to replace the human workforce in the kitchen and tarnish the source of income for thousands of workers? It's an obvious question, however, it currently has no answer.
Right now, automation is just "lending a hand" in the restaurant industry, with robotic equipment assisting people in repetitive and easy-to-do tasks like flipping burgers and pumping out espresso shots, unable to perform the whole task independently.
Most industry experts, like Patrick Maguire from Servant Not Servant, believe that the idea of automation from the standpoint of economic & operational efficiency may be relevant, however, machines can never match up to the personal touch and intangible service skills that humans bring to the dining experience.

Similarly, Restaurant Opportunities Centers United co-founder, Saru Jayaraman says that she is yet to witness robots replace humans completely in the restaurant industry and that a boom in automation could actually lead to increased restaurant employment in the future, with data suggesting a 45% growth in restaurant employment in California from 2001 to 2016.
However, a few decades ago, even the idea of having robot-prepared pizzas would have seemed bizarre, and yet, today it stands as a reality. Whether automation will ever completely overtake the restaurant industry, that's a story only time can tell.
Conclusion
There's no way around it: automation in the restaurant industry is gaining speed quickly, and it's here to stay. This approach is one of many technologies and strategies that businesses are using to keep up with high operational costs and increasing competition.
Companies that are pioneering this new technology are exploring how to balance the pros and cons of integrating it into their business model – finding just the right mix of rapid, repeatable automation and the high-level decision-making skills and human touch that robots simply can't replace.



 Source
Source







.webp?width=144&height=72&name=Eat%20App%20Logo%20(3).webp)