Running a successful restaurant requires a two pronged approach. On one hand, it's about serving delicious food and helping people experience and build great memories with each other. On the other hand though, it's also about maintaining restaurant operations with the help of various restaurant metrics for sales, revenue, staff and more.
Restaurateurs often prioritize the food side of running a business and don't pay enough attention to their restaurant metrics. They miss out on valuable insights and opportunities by running restaurants based solely on intuition.
While great experience and industry knowledge is invaluable, if the only restaurant metrics you use in planning out your restaurant strategy is total sales, there’s a lot of scope for improvement.
Restaurant performance metrics provide an objective view of how different parts of the business are performing - what’s doing well and what’s going wrong. This helps restaurant owners take better decisions to improve performance and improves business planing.
In this article, we will go through the most important restaurant metrics that you should be using at your restaurant.
The most important restaurant metrics to track
We've compiled the most important restaurant metrics you need to incorporate into your daily reporting as a restaurant owner.
1. Cost of Goods Sold (CoGS)
What does Cost of Goods Sold measure?
Cost of Goods Sold (CoGS) is the total cost of all the ingredients used to create dishes sold at a restaurant in a given period of time. However, it does not take into account one-time costs like utility bills, new chairs, and repairs.
In case of full-service restaurants, CoGS should ideally only include consumable products. All the other products used in the process of selling, like paper boxes, cutlery, straws, etc. should be accounted for in a different purchasing budget to streamline the inventory and purchasing process.
Calculating CoGS accurately is highly dependent on proper inventory management as it’s about tracking ingredients. If the inventory is not counted properly, the final cost will not be correct.
Why is Cost of Goods Sold important to measure
CoGS helps understand the actual cost of food over a period of time. Unlike theoretical food cost, it also takes into account wastage, shrinkage of inventory, or other external factors. Calculating the variance between the two can give you an idea about the food that does not end up on plates and hence, does not make you money.
CoGS is one of the components of prime costs, and therefore, plays a very important role in maintaining restaurant performance.
Interested in learning more about CoGS? Here’s a video by Restaurant Accounting Service Inc. to give you more insights about how it works.
How to calculate Cost of Goods Sold
Start of the Month Inventory + Additional Purchases - End of the month Inventory = CoGS
2. Labor Costs/Labor Cost Percentage
What does Labor Cost measure?
Labor cost determines the total amount of money spent on labor at your restaurant, including salaries, taxes, overtime and employee benefits. Labor makes up for one of the biggest costs at a restaurant, usually second only to rent.
Because labor cost includes many variables, it can be helpful to split it by roles to get a more accurate picture. Group together positions that have the same payment type (hourly or salary pay) so that you can calculate the costs more accurately.
How to calculate Labor Cost
Employee Wages + Employee Benefits + Taxes = Total Labor Cost
Once you have your labor costs, the next step is to calculate the percentage of your average revenue that is spent on labor. A healthy labor cost falls between 20-35% of revenue. Any higher than that will affect your overall restaurant profitability
Labor cost/Total Revenue = Labor Cost Percentage
Labor cost is the second component of your restaurant’s prime cost (after CoGS), which is why it’s important to accurately
3. Prime Cost
What does Prime Cost measure?
Prime cost is calculated by combining the two biggest costs at your restaurant - cost of goods sold and labor costs.
Why is Prime Cost important to measure
As it represents your largest expenses, prime cost has a significant effect on your overall operations - from your pricing strategy, to staff scheduling, marketing budget, and everything else. If you’re looking to reduce costs or maximize profits, aiming to decrease prime costs is the best way to do it.
A good prime cost should range around 60% of your entire restaurant costs. Anything higher than that will eventually affect your profitability, and anything lower than that will affect your quality as it means you’re not spending enough on ingredients or labor, or both.
How to calculate Prime Cost
CoGS + Labor Cost = Prime Cost
4. Overhead Expenses
What does Overhead Expenses measure?
Overhead costs include all the other operational costs of running a restaurant that are not included in prime costs. These include fixed and variable expenses that are necessary for restaurant operations, apart from food and labor.
Some examples of overhead costs are:
-
Promotional/marketing costs
-
Rent/mortgage payments
-
Taxes
-
Repairs and maintenance
-
Utilities
-
Licensing fee
Why are Overhead Expenses important to measure
Calculating overhead costs is necessary to determine your pricing structure. The price of your menu item must be able to cover both the prime and overhead costs. If it’s unable to do so, then your costs will be higher than your average revenue, and you will not be able to reach the break even point. It allows you to better understand where you’re spending your money and how you can improve profitability (by reducing costs or increasing prices).
How to calculate Overhead Expenses
Rent + Marketing costs + Taxes + Licensing fee + Repairs + Utilities + Other Expenses = Overhead Costs
5. Variable and Fixed Costs
What do Variable and Fixed Costs measure?
A restaurant’s total costs consist of fixed and variable costs. Fixed costs include things like rent, salary, capital investment etc. that remain unchanged overtime. Variable costs, on the other hand, are constantly changing and growing with your business. These include cost of ingredients, dynamic labor costs (labor that changes regularly, like staff that works on an hourly basis, or part-time employees), marketing costs, and more.
Why are Variable and Fixed Costs important
Knowing exactly how much of your total cost is fixed and variable can be helpful in identifying areas of improvement. Fixed costs tend to take the bigger share as they include heavier costs like mortgage or rent. By tracking the percentage of variable costs in your total cost over time can keep you updated about any significant changes.
How to calculate Variable and Fixed Costs
Fixed Cost/Total Cost x 100 = Percentage of Fixed Cost in Total Cost
Variable Cost/Total Cost x 100 = Percentage of Variable Cost in Total Cost
6. Food Cost Percentage/Food Costs
What does Food Cost measure?
Food cost percentage is a commonly used restaurant metric. Food cost is the total cost of ingredients used to prepare an item, while food cost percentage is the part of the menu item's price taken up by its food cost.
Why is Food Cost important to measure
Food cost helps you determine whether your menu prices are able to cover the cost of running your restaurant. If it’s very high, it means that your menu prices are not able to make up for the cost, and your profit margin on the item is very low.
The ideal food cost percentage at fine-dining restaurants falls around 35%, while casual dining falls around 30%. At this range, your menu prices can be set at a level that makes your restaurant money without passing on too many costs to your customers or sacrificing food quality.
How to calculate Food Cost
To calculate the food cost percentage of a dish you need to find the cost of a single serving and divide it by its sales price and multiply it by 100.
Food cost percentage = cost of all ingredients/sale price x 100
For example, if the price of a dish is $18 and its food cost is $6, food cost percentage is: 6/18x100= 33.
7. Cash Flow
What does Cash Flow measure?
A restaurant's cash flow statement captures cash receipts and payments over a defined time period, typically a quarter or fiscal year. Simply put, your restaurant's cash flow is your profit minus all operating expenses.
Why is Cash Flow important to measure
The right staff, passion for good food, and perseverance are all necessary for starting and operating a successful restaurant, but even the best-laid plans will fall flat without one vital component - cash.
The amount of money coming into and leaving your restaurant, as well as the amount of cash you have on hand, are two of the most critical things to monitor as a restaurant. If you don't regularly evaluate your cash flow, you might be dooming your restaurant to failure.
How to measure Cash Flow
Cash Flow = Beginning Cash - Ending Cash
8. Total Sales
A restaurant’s total sales are a great indicator of its performance. The higher the sales, the higher the total revenue. Measured against a restaurant’s break-even point, it helps understand whether it’s doing good enough, or requires improvement to increase profitability. If your restaurant’s total sales are below the determined break-even point, you will not be able to reach profitability. Therefore, knowing exactly how much you’re selling is very important to evaluate performance.
The total sales of a restaurant can be easily calculated through its POS system. To better understand your restaurant performance, dig deeper into this number to find out which of your menu items are doing well and which menu items might need to be updated.
9. Gross Profit
What does Gross Profit measure?
This refers to the amount of money earned by your restaurant after deducting the cost of goods sold from the total revenue.
Why is Gross Profit important to measure
It’s important to measure as it tells you how much money you have available from your revenue to pay labor and other overhead expenses. It’s a key indicator of how well your restaurant is performing. If your restaurant’s gross profit is lower than its labor and overhead costs, you’re not making enough money and will remain in a state of loss.
How to calculate Gross Profit
Total Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold (CoGS) = Gross Profit
Gross Profit is also calculated as a percentage or margin of profit from the total revenue, i.e., the percentage of your revenue that makes up gross profit.
Gross Profit/Total Revenue x 100 = Gross Profit Margin
For example, Total revenue $150,000 - CoGS $55,000 = Gross profit $95,000.
Gross Profit Margin = $95,000 / $150,000 x 100 = 63%
A well-performing restaurant should have a gross profit margin of around 70%
10. Net Profit
What does Net Profit measure?
Net profit refers to the amount of money earned by your restaurant after deducting all costs including cost of goods sold, labor costs, and overhead expenses (including taxes). It tells you exactly how profitable your restaurant is.
Why is Net Profit important to measure
Knowing your restaurant’s profitability is important to make strategic decisions. High profitability indicates that your current restaurant operations are working well, and opens a world of opportunities for the future. However, a low profitability means that you need to take a step back and understand what’s going wrong, and make changes to improve your restaurant performance.
How to calculate Net Profit
Gross Sales - Prime Costs - Overhead Expenses = Net Profit
Like gross profit, net profit is also calculated as a percentage or margin of profit from the total revenue i.e., the percentage of your revenue that makes up net profit.
Net Profit/ Gross Sales = Net Profit Margin
Profit margins vary from restaurant to restaurant, but 6% is considered a good average.
11. Break-Even Point
What does Break-Even Point measure?
Break-even point refers to the amount of revenue required to cover restaurant costs.
Why is it important to measure Break-Even Point
It’s a key indicator of a restaurant’s performance and indicates whether it has reached profitability or not. If your restaurant is not reaching break-even point regularly, you will not be able to generate profit.
How to calculate Break-Even Point
Total Fixed Costs / (Total Sales - Total Variable Costs/Total Sales) = Break- Even Point
For instance, if your total fixed and variable costs are $4,000 and $2,000 respectively for the month, and your total sales come up to $8000, the break-even point for the month will be 4,000/(8,000-2,000/8,000) = $5,333
While fixed costs are easy to calculate, the variable costs that change regularly (like marketing or packaging costs) can make break-even point calculations complicated.
12. Average Check Size
What does Average Check Size measure?
The average check size measures the average amount a customer spends during a visit at a restaurant.
Why is Average Check Size important to measure
It helps understand how well your staff is able to sell to customers and also gives an idea of how many customers are required to meet your daily revenue goals and break-even point.
How to calculate Average Check Size
Total Sales/Number of Customers = Average Check Size
For higher accuracy, the average check size for each shift should be calculated separately, as it’s likely to vary between lunch and dinner.
Further reading
13. Contribution Margin
What does Contribution Margin measure?
Contribution margin refers to the net amount of money that each menu item contributes to your restaurant revenue. It indicates which of your dishes are earning you the most money.
Why is Contribution Margin important to measure
Food cost percentage and contribution margin are different metrics and don't always go in the same direction.
A dish with a low food cost percentage will be more profitable. However, that doesn't mean it will necessarily create a higher contribution margin.
In fact, a dish with a higher food cost percentage may have a higher contribution margin because it sells more frequently and therefore contributes more money to your revenue.
What's more, while food cost percentage is a relative metric, contribution margin is a real number.
For instance, an item like fries that sells at $2 and costs $0.25 to make, has a very low food cost percentage (12.5%), but a contribution margin of just $1.75. A steak that sells at $25 and costs $17 has a high food cost percentage (68%), but its contribution margin ($8) is 4.5 times higher than the fries.
Knowing the contribution margin of each item can help determine which dishes are the biggest revenue boosters, and the ones that need to be tweaked, or taken off the menu.
14. RevPASH
What does RevPASH measure?
RevPASH refers to Revenue Per Available Seat Per Hour. This metric calculates the performance of your dining room by taking into account revenue, seats, and time altogether.
Why is measuring RevPASH important
Calculating RevPASH helps most restaurants optimize seating, increase guest spend and improve your overall dining room occupancy and revenue.
Read more: Grow Your Restaurant Revenue with the RevPASH Formula
How to calculate RevPASH
RevPASH can be calculated by picking a period of time and dividing the revenue for that period by the number of seating hours (number of available seats/number of hours in a chosen time period).
Revenue in a Given Time Period/ (Number of Hours/ Number of Seats) = RevPASH

15. Employee Turnover Rate
What does Employee Turnover Rate measure?
Employee turnover rate is the frequency at which staff leaves your restaurant over a given period of time. This includes retirement, firing, and resignations.
Why is Employee Turnover Rate important to measure?
It’s important to know how often your staff is leaving, as turnover costs both time and money, and can significantly affect your net profit. A high employee turnover rate may indicate a problem in your work culture or in your hiring process. Due to the high cost of hiring, it’s important to keep your restaurant’s employee turnover rate as low as possible.
How to calculate Employee Turnover Rate?
Number of Employees Departed/ Average Number of Employees x 100 = Employee Turnover Rate
16. Total Sales by Server
Total sales by server refers to the volume of dollar amount a server is responsible for in a given period of time. It helps restaurant owners get an insight into the performance of individual servers. Comparing the total sales of each server can help identify the ones that require some more training or need to be replaced to improve overall restaurant operations.
17. Sales Per Labor Hour
What does Sales Per Labor Hour measure?
This metric gives a breakdown of the average number of sales made collectively by the employees at a restaurant.
Why is Sales Per Labor Hour important to measure?
It helps understand the productivity level of your staff and whether you are getting a good return on investment for your labor costs. You can also use this metric to compare productivity levels of different staff members and make decisions accordingly. A good sales per labor hour depends on the type of restaurant. Casual restaurants tend to have high productivity levels with low labor costs, while higher-end restaurants, due to their premium service have less productivity with higher labor costs.
How to calculate Sales Per Labor Hour?
Total Sales in a Given Time Period/ Number of Hours in the Given Time Period = Sales Per Labor Hour
18. Table Turnover Rate
What does Table Turnover Rate measure?
Table Turnover Rate refers to the average number of times tables are occupied in a given time period. Knowing your table turnover rate is crucial for optimizing your restaurant’s capacity. A low turnover rate indicates that your tables are not being used to their maximum potential and you could increase the number of guests served.
Why is Table Turnover Rate important to measure
Having a high turnover rate is the goal, however, it’s important to find the balance between turning tables and maintaining customer service.
Being aware of your restaurant's average table turnover rate helps track performance and take strategic decisions to improve operations. A bad table turnover rate can have a significant impact on your revenue, so make sure you pay attention to this number.
A good table turnover rate differs between restaurants. Fine-dining restaurants usually have a lower turnover rate compared to casual restaurants as guests are paying a premium price for better service.
How to calculate Table Turnover Rate
No. of parties served in a given time period/No. of tables = Table Turnover Rate
19. Times Per Table Turn
What does Times Per Table Turn measure?
Time per table turn calculates the average amount of time a table is seated for. It helps most restaurants understand if the tables are being turned fast enough by the servers, and also provides an estimate of how many parties can be seated within a shift (total guests served).
Why is measuring Times Per Table Turn important
Knowing this number can also help servers provide a more accurate waiting time and allow the host/hostess to better understand if they can accommodate more walk-ins. It also tells you if guests are spending too much time on the table.
How to calculate Times Per Table Turn
(Number of Parties Served in a Shift/ Number of Tables)/ Number of Hours in a Shift = Time per Table Turn
For instance, if a restaurant has served 30 parties in a 2 hour shift, and has 12 tables, the time per table turn will be (30/12)/2 = 1.25 hours i.e. 1 hr 15 mins.
20. Inventory Turnover Ratio
What does Inventory Turnover Ration measure?
Inventory Turnover Ratio is the number of times a restaurant replenishes its entire inventory/stock over a specific period of time.
Why is Inventory Turnover Ratio important to measure
Inventory Turnover Ratio play an important role in food ordering, food costs, recipe costing, and menu pricing. For this reason, it is important to calculate and understand the average turnover of a restaurant's food inventory over time. Not only does it give you a better view of your entire inventory, it also helps improve your business and profits.
How to calculate Inventory Turnover Ratio
Average Inventory = (Beginning Inventory + Ending Inventory) / 2
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Cost Of Goods Sold / Average Inventory
How to track guest metrics
21. Customer Retention Rate
What does Customer Retention Rate measure?
This metric tells you the percentage of return customers in your total customer count. Regular customers are one of the best sources of increasing revenue at a restaurant. As per a Harvard study, just a 5% increase in regular customers can improve profit up to 125%, which makes it crucial to track this number.
Why is Customer Retention Rate important to measure
A low customer retention rate indicates issues in your restaurant operations. Is it the food, the service, or something else? Dig deeper to find the root cause for people not returning and take actions to fix the issue
How to calculate Customer Retention Rate
(Total Customers-Total New Customers) /Total Customers x
22. Customer Acquisition Costs (CAC)
What does Customer Acquisition Cost measure?
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is a restaurant marketing metric that tells you how much it costs to bring in a new customer to your restaurant. It helps set a benchmark as to whether or not your restaurant marketing strategy is effective.
Why is Customer Acquisition Cost important to measure
By calculating different customer acquisition costs, you can prioritize marketing strategies that maximize your return on investment. In the restaurant industry, this metric is super important to evaluate your marketing performance. Monitoring your customer acquisition costs can also help identify which channels are most cost-effective when acquiring new customers. Social media advertising may be a cheap way to acquire customers. However, if you are entering this market quickly and find that search engine advertising or Google advertising is bringing in more new guests at a slightly higher cost, you need to change your approach.
How to calculate Customer Acquisition Cost
Customer Acquisition Cost = Total Spent on Marketing / Total Number of New Customers
23. Reservations Per Day
What does Reservations Per Day measure?
Reservations Per Day is a measure of how many raw reservations your restaurant generates daily. This metric does not filter out non materialized reservations (no-show, canceled, denied, etc) but rather measures every single reservation your restaurant has received.
Why is Reservations Per Day important to measure?
Reservations Per Day is super important for a data-driven restaurant to track as it is the only way to understand trends and improvements over time. Reservations Per Day is a core metric that tells you if your marketing campaigns have worked, your specials brought in more customers and if you are losing reservations for one reason or another.
How to measure Reservations Per Day?
If your reservation software has built-in advanced reporting, this metric will be very easily accesible without needing to make any calculations.
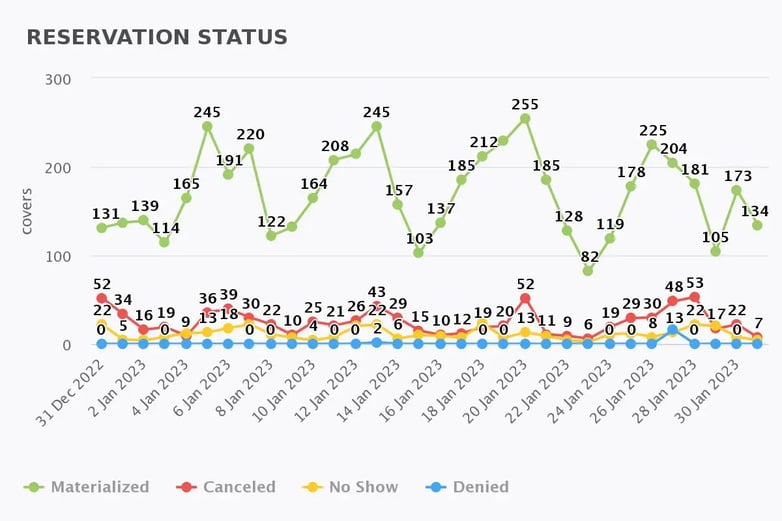
24. No-Show Rate
What does the No-Show Rate measure?
A restaurant's No-show rate is a measure of how many bookings did not show up to their reservation in a time period compared to the total reservations in the same time period.
Why is the No-Show rate important to measure?
No-shows are one of the biggest hurdles a restaurant must overcome to be successful. It's important to keep an eye on your restaurant's no-show rate, given its significant impact on sales. A good no-show rate differs from restaurant to restaurant. Set a benchmark for your restaurant based on factors such as type of restaurant, size of tables, target audience, etc.
Most guests are completely unaware of the consequences for restaurants when they don't show up to their reservations. In their eyes it is just a table. Leave it empty and surely someone else will fill the table.
Unfortunately it doesn't work that way. Restaurants cannot release a reserved table to another guest for at least 15-20 minutes after the reservation time. If it leads to no-shows, you lose revenue for your table. This is a big problem for restaurants. Empty tables are a black hole in sales, especially in fine dining restaurants. For example, at a Michelin-starred restaurant, two no-shows could cost operators 100% of the profit.
By understanding what your restaurant's average no-show rate is, you can start to work towards reducing it.
How to calculate No-Show Rate?
No-Show Rate = Number of No-Show Reservations / Total Reservations
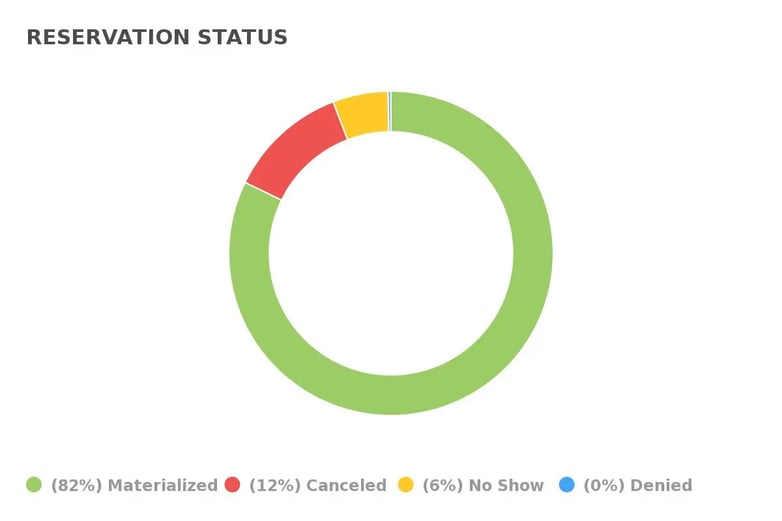
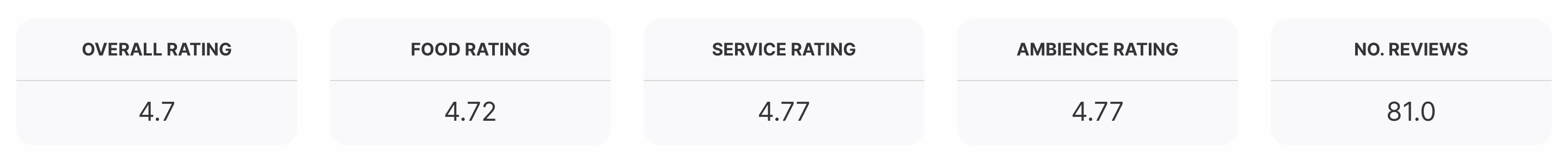
25. Average Rating Score Per Month
What does Average Rating Score Per Month measure?
Average Rating Score Per Month is a monthly average of all your customer's reviews after dining at your restaurant.
Why is Average Rating Score Per Month important to measure
Customer feedback is now more important than ever in the restaurant industry's increasingly competitive environment. To gain thorough insights into your restaurant's performance and gain a competitive edge, it is now imperative to collect data on the experience of your customers.
How to calculate Average Rating Score Per Month
If your restaurant uses a reservation system that has built-in automated guest surveys, you will be able to generate an Average Rating Score Per Month directly within your chosen software.
FAQs
What is a restaurant metric or KPI?
Restaurant metrics provide an unbiased view of how various aspects of a restaurant are performing - what is working and what needs improvement. This helps restaurant owners in making smarter decisions that improve performance.
What are the 5 key performance metrics to track in a restaurant?
- Break-Even Point
- Food Cost Percentage
- Average Check Size
- Contribution Margin
- Table Turnover Rate
What are 5 restaurant marketing metrics?
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Feedback Score
- Reservations Per Day
- No-show Rate
- Average Rating Score Per Month
How to calculate benchmarks for restaurant labor cost?
You can calculate restaurant labor cost with the following equation:
Total Labor Cost = Employee Wages + Employee Benefits
Once you have your labor costs, the next step is to calculate the percentage of your revenue that is spent on labor. A healthy labor cost falls between 20-35% of revenue. Any higher than that will affect your overall restaurant profitability
Labor Cost Percentage = Labor Cost/Total Revenue















%20(1).jpg?width=200&name=eatapp3%20(1)%20(1).jpg)
-1.png?width=1812&height=1072&name=TripAdvisor%20%26%20More%20Bookings%20(1)-1.png)
-2.png?width=1812&height=1072&name=Google%20Bookings%20(1)-2.png)
.webp?width=200&name=reserve_with_google%20(1).webp)
.jpeg?width=200&name=Eat%20App%20Co-founders%20(2).jpeg)
-1.png?width=200&name=TripAdvisor%20%26%20More%20Bookings%20(1)-1.png)
-2.png?width=200&name=Google%20Bookings%20(1)-2.png)
-1.png?width=200&name=Instagram%20Bookings%20(1)-1.png)
-1-png.webp?width=200&name=Facebook%20Integration%20Rectangle%20(1)-1-png.webp)







.webp?width=200&name=download%20(1).webp)
%20(1)-2.webp?width=200&name=Eat%20(34)%20(1)-2.webp)
%20(1)-2.webp?width=200&name=Eat%20(18)%20(1)-2.webp)












.webp?width=144&height=72&name=Eat%20App%20Logo%20(3).webp)