A restaurant business plan is a framework that guides you to plan and forecast every element of restaurant management and operations. This includes anything from your restaurant's menu design, location, financials, employee training, and a lot more.
Creating a solid business plan is important, as it helps:- Transform your restaurant ideas into reality.
- Boosts entrepreneurial success by 16% (Harvard Business Study).
- It equips you to navigate challenges before they arise.
- Attracts potential investors.
Planning is key to restaurant success. Without a plan, you're more likely to join the 60% of restaurants that fail within a year. Many businesses fail due to lack of preparation and effective planning, making a comprehensive business plan essential for survival.
While planning helps you avoid common pitfalls, it also positions you to take advantage of the booming restaurant climate. The already booming restaurant climate offers unique opportunities for new restaurants to thrive if they are well-prepared.
Create a business plan to set yourself up for success. Here's how to get started.

What is a restaurant business plan?
Before writing a restaurant's business plan, it is important to understand its fundamentals. It serves as a roadmap for starting and running your restaurant, making it easy for outside parties, such as investors, to understand your objectives, vision, and plan of action for your restaurant.
A well-prepared restaurant's business plan acts as a guiding document for restaurant owners, helping to attract investment, reduce the risk of failure, and ensure successful operations through detailed and well-researched planning.
Business plans vary in length and level of detail, ranging from brief synopses to large papers. Investors can benefit from clear insights and additional information provided by beginning with a concise plan and working their way up to a detailed one.
In short, your business plan should include a thorough description of the resources allocated to your restaurant’s success.
Every business should have a business plan, whether new or existing. Business plans help you focus on your goals and can help you get back on track if you stray from them.
Why is a restaurant business plan important?
It’s unlikely that you would be able to secure an investor to help fund your restaurant dream without a proper plan. And even if you do, the lack of proper planning, regulations, and forecasts will set your restaurant up for failure.
Your restaurant business plan is what is going to map out how you plan on turning a profit from your business, as well as where your restaurant fits into the saturated market and how you plan on standing out.
Identifying your competitive advantage, which sets your restaurant apart from local competitors, is important for capturing market share and succeeding in a crowded marketplace.
For any new business, especially in the industry, thorough preparation and a well-structured plan are essential to avoid the high failure rate. A little time and pain early on are worth the reward of a successful restaurant in the long run.
You have to show any potential investor that you have an actual plan, you know what you’re talking about, it looks professional, and you’re not just screwing around.
What every plan should include
Whether this is your first business plan or your 10th, using a template specifically designed for the restaurant industry can be incredibly helpful. Our restaurant business plan template includes all the necessary sections you need. You can download a customizable copy of the business plan template here.
To craft your own restaurant business plan, make use of available resources and samples to ensure your plan is detailed and effective.
Conducting a thorough market analysis to understand customer demographics and competition is crucial for the success of your restaurant. Keep reading to learn about the key elements that make a restaurant business plan successful.
Further reading
Steps to include in your business plan
Your restaurant business plan should represent your brand and goals, and you don’t have to build it from the ground up.
Pro tip: Use a professionally crafted template filled with actionable insights to help you create a profitable strategy.
Whichever approach you take, your business plan should cover 12 key components. Creating realistic financial projections is crucial to ensure the financial feasibility of your restaurant.
As part of your planning process, estimate costs and pricing menu items to create financial projections that guide your restaurant toward profitability and sustainability.
Here’s a breakdown of the essentials for a successful restaurant plan:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- Market Analysis
- Menu
- Employees
- Restaurant Design
- Location
- Market Overview
- Marketing
- External Help
- Financial Analysis
- Legal Compliance
1. Executive summary
A restaurant business plan should always begin with an executive summary. Why?
- 80% of venture capitalists say they read the summary first.
- 62% of investors say they would not continue reading your plan if the executive summary did not capture their interest.
- A strong executive summary can increase the likelihood of securing funding by up to 40%.
An executive summary is your restaurant business plan’s introduction and quick pitch. It’s created to grab attention, especially from investors, and guide them into the full plan. Beyond summarizing your concept, it helps define your restaurant’s identity, shaping customer experience and setting you apart from competitors.
To stand out, focus on key elements that make a strong executive summary:
- A mission statement
- Proposed concept development
- Cuisine selection
- The overall execution
- The potential costs
- Expected return on investments (ROI)
- Business succession plan
A well-conceived mission statement can provide a guiding light to keep your restaurant moving in the right direction. It helps ensure that every decision you make and every interaction you have is in line with your core values and goals.
Let's take a more in-depth look at the concept development, cuisine selection, and mission statement.
- 1.1 Concept Development
Selecting the type of restaurant, service style, and atmosphere is the first step towards creating a unique dining experience. Whether you envision a sample menu for a:
- Cozy, intimate bistro
- Bustling quick-service deli
- Fast-casual restaurant
- Fine dining establishment
Your concept should reflect your passion and expertise in the industry. Studying business plans from other restaurants can provide valuable insights into layout options and effective communication styles.
%20(1).webp?width=800&height=457&name=Restaurant%20development_Eat%20App%20(1)%20(1).webp)
- 1.2 Cuisine Selection
The cuisine you select for your restaurant can significantly influence its success. Choosing the appropriate cuisine is vital for distinguishing your establishment from competitors and attracting your target customers.
To make an informed decision, consider factors such as:
- Market demand
- Expertise and passion
- Ingredient availability
- Competition
- Profitability
- Cultural fit
- Seasonality
- Dietary restrictions and trends
-
Detailed cost analysis
In the highly competitive restaurant industry, keeping track of current and emerging cuisine trends can be a significant advantage.
- 1.3 Creating a mission statement
A mission statement is your restaurant’s compass - it highlights your purpose, values, and goals while resonating with both investors and customers. It also inspires your team, guiding their efforts toward your vision.
To create a statement that truly stands out, follow these steps:
- Identify the purpose of the restaurant.
- Contemplate the brand’s image.
- Account for the target audience.
- Incorporate company values.
- Ensure brevity and comprehensiveness.
Related content: How to Write a Restaurant Mission Statement
Remember, your statement should not only differentiate your restaurant from competitors but also resonate with your target market.
2. Business description
This is where you carefully introduce the company in the restaurant business plan (and overall business model).
Begin with a brief overview of the management team, highlighting their credentials, relevant experience, and personal values to establish credibility and trust with potential investors. Include the name of the restaurant you are launching in this field, along with its address, phone number, and other important information.
When discussing the credentials and experience of business partners, consider how a management team write can effectively present your leadership team. Focus on showcasing each member's strengths and relevant background to build investor confidence.
Further reading
Then, include the owner's information and a synopsis or explanation of their background. Additionally, highlight the credentials and experience of the business partners to build trust with potential investors.
The second section of the restaurantre description should outline the restaurant's legal position and its short—and long-term objectives.
Here's an example of the layout:
Company Description
Restaurant Name: [Restaurant Name]
Location: [Restaurant Address]
Contact: [Restaurant Phone Number] | [Restaurant Email Address]
Owner: [Owner Name]
Experience: [Owner Name] has over [Number] years of experience in the industry. They have worked in various roles, including [List of Roles]. They are passionate about food and creating a memorable dining experience for their guests.
Legal Standing: [Restaurant Name] is a [Type of Legal Entity] registered in [State/Province].
Pro tip
Feel free to add this into ChatGPT or Gemini to help you craft a business description section within your business plan.
Further reading
3. Analysis for your target market
The analysis portion of the restaurant business plan is usually divided into three parts.
- Industry analysis
Understanding your position among competitors is essential for developing effective marketing strategies and ensuring your restaurant stands out.
This section aims to explain your target market to investors and why you believe guests will choose your restaurant over others. When differentiating your business, it is essential to clearly present your restaurant concept—describe your overall vision, unique identity, and what sets you apart from others in the market.
An example of analyzing your target market
Comprehending your target market is key to customizing your restaurant offerings to their preferences and needs.
By diving into demographics, preferences, dining habits, and trends, you can fine-tune your concept and marketing strategy to reach and appeal to your target audience effectively.
Identifying your primary target market involves considering factors such as:
- Age
- Interests
- Average Income
- Location
Then, let's take a look at our second part of the analysis.
- Competition analysis
It's easy to assume that everyone will visit your new restaurant first, so it's important to research your competition to make this a reality.
What direct competitors have already established a customer base in the area? Take note of everything from their prices, hours, and service style to menu design to the restaurant interior.
Then explain to your investors how your restaurant will be different.
- Advertising analysis
Your investors are going to want to know how you plan to market your restaurant. How will your marketing campaigns differ from what is already being done by others in the restaurant industry?
How do you plan on securing your target market? What kind of offers will you provide to your guests? Make sure to list everything.
4. Menu
The menu is the most important part of a restaurant's debut. Your restaurant wouldn't be able to operate without it.
You most likely don't have a final draft at this time, but you should aim to create a mock-up menu for your restaurant business plan. Remember, the menu is more than just a simple list of food items; it should be a carefully designed representation of your restaurant's brand.
You can choose a design that you can envision yourself using and add your logo to the mock-up.
There are several resources available online if you need assistance with menu design or don't want to hire a designer.
But the price should be the most important component of your sample menu. The cost research you've completed for investors ought to be reflected in your prices. They will have a clearer idea of your restaurant's intended price range as a result.
You'll quickly see how important menu engineering can be, even early on.
5. Employees
The company description section of the restaurant business plan briefly introduces the owners of the restaurant with some information about each. This section should fully flesh out the management team.
The investors don’t expect you to have your entire team selected at this point, but you should at least have a couple of people on board. Use the talent you have chosen thus far to highlight the combined work experience everyone is bringing to the table.
Most independent restaurant investors are especially interested in the personal values, motivations, and backgrounds of the management team, seeking stories that reveal what drives their passion for restaurant ownership.
Emphasize the strength of your management team to attract independent restaurant investors who value personal values and ethos alongside financial returns. Restaurant owners should ensure their business plan is comprehensive, covering all essential aspects to justify their ideas and set a strong foundation for success.
6. Restaurant design
The design section of your restaurant business plan showcases your vision to investors. If you don’t have professional renderings, a mood board with images that reflect your desired aesthetic works well.
Remember, design includes more than looks; it covers everything from software to kitchen equipment. Additionally, the design should enhance the guest's service experience, whether through efficient counter service or a more theatrical dining experience.
%20(1).webp?width=800&height=457&name=DALL%C2%B7E%202025-01-08%2013.46.59%20-%20A%20visually%20appealing%20image%20of%20a%20restaurant%20business%20plan%20design%20concept%2c%20featuring%20a%20mood%20board%20with%20various%20aesthetic%20elements%20such%20as%20modern%20restaur%20(1)%20(1).webp)
7. Location in the restaurant industry
The location you settle on for your restaurant should be well aligned with your target market (making it easier to cater to your ideal customer) and with your business plans. High foot traffic in the area can significantly boost your restaurant's visibility and attract more customers.
At this stage in the process, it's not uncommon not to have a specific location in mind, but you should at the very least have a few options to narrow down.
Pro tip
When you approach your investors about potential locations, make sure to include as much information as possible about each venue and why it would be ideal for your brand.
Further reading
8. Market overview
The market overview builds on your research by covering both local and broader economic conditions. Highlight any challenges, such as economic downturns, and how you plan to address them. Having well-defined pre- and post-opening marketing plans is crucial to attract investors and maintain momentum.
Identify competing restaurants and explain how you’ll differentiate your concept.
9. Marketing
With restaurants opening left and right nowadays, investors are going to want to know how you will get the word of your restaurant to the world.
The next marketing plan and publicity section should go into detail on how you plan to market your restaurant before and after opening. It should also highlight strategies to engage both new and existing customers, ensuring they feel valued and encouraged to return.
As well as any plans you may have to bring a PR company on board to help spread the word.
Read more about creating a restaurant marketing plan: How to write a restaurant marketing plan from scratch
10. External help
To make your restaurant a reality, you are going to need a lot of help. List any external companies or software you plan on hiring to get your restaurant up and running.
This includes everything from accountants and designers to suppliers that help your restaurant perform better, like POS systems and restaurant reservation systems.
Hiring an accountant with a restaurant-centric practice is crucial to ensure they understand the specific financial needs and challenges of running a restaurant.
Explain to your other potential investors about the importance of each and what they will be doing for your restaurant.
This specialized expertise ensures your accountant is deeply familiar with the unique aspects of restaurant finances, rather than having only general experience.
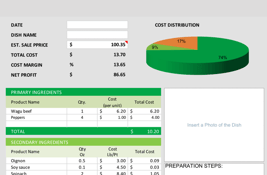
11. Financial analysis
The most important part of your restaurant business plan is the financial section. We would recommend hiring professional help for this given its importance.
Hiring a trained accountant will not only help you get your own financial projections and estimates in order but also give you a realistic insight into owning a restaurant. You should have some information prepared to make this step easier for the accountant.
He/she will want to know how many seats your restaurant has, what the check average per table will be, and how many guests you plan on seating per day. Additionally, including a profit and loss statement is crucial for projecting your financial outlook and satisfying investor requirements.
After estimating costs and pricing menu items, you can use this information to create financial projections that help forecast profitability and ensure operational sustainability.
In addition to this, doing rough food cost calculations for various menu items can help estimate your profit margin per dish. This can be achieved easily with a free food cost calculator.
12. Legal compliance
Legal compliance is essential for restaurant success, covering food safety, health codes, licensing, and employment laws. Including this in your plan shows professionalism, reduces risk, and reassures investors. Establishing a sustainable business structure with the guidance of an attorney ensures long-term viability and success for your business.
It also helps you avoid legal issues and stay focused on running your restaurant smoothly.
Need a ChatGPT prompt to get started?
To create a restaurant business plan, you can use the following prompt:
Create a detailed restaurant business plan that includes the following sections:
- Executive Summary: Overview of the restaurant's concept, mission, and vision.
- Business Description: Type of restaurant, target market, and food & beverage offerings.
- Market Research: An analysis of local competitors, customer demographics, and market trends.
- Marketing Strategy: Approach for attracting and retaining customers, including promotions and digital presence.
- Operations Plan: Daily operations, staffing needs, supplier information, and any technology integrations (e.g., POS systems).
- Financial Plan: Projected startup costs, revenue forecasts, break-even analysis, and funding requirements.
- Management and Ownership: Team structure and roles, ownership model, and leadership approach.
Pro tip: Just be aware that your AI-generated restaurant business plan will appear very generic. Fill in all the relevant blanks, and add personality to the mix.
Consider reviewing restaurant business plan examples to gather ideas and ensure your plan is comprehensive and appealing to potential investors.
How to sell a restaurant idea
Once your business plan is ready, become its expert; investors expect you to know it inside out. Share it with your network, and if interest sparks, be ready to meet. Some may ask for a pitch presentation, so prepare a polished slide deck and practice it thoroughly.
Remember, investors often seek more than just money; showcasing your personal values and the character of your management team can make your pitch more compelling. Be ready for all types of questions, and if unsure, it’s okay to follow up with answers later.
%20(1)-1.webp?width=800&height=450&name=Eat%20(87)%20(1)-1.webp)
Takeaways
A well-crafted restaurant business plan is the backbone of your restaurant’s success, providing clarity on everything from the concept to the customer experience.
By taking the time to carefully map out each part, you set yourself up for easier access to funding, stronger customer appeal, and greater chances of achieving your goals.
A comprehensive restaurant business plan thoroughly identifies and analyzes business opportunities, serving as a strategic blueprint for long-term success.
Remember, your business plan isn’t set in stone, it’s a tool that should grow with your business. Regularly updating it ensures you're staying on track and adapting to new opportunities and challenges.
FAQs
Why is a restaurant business plan important?
A restaurant business plan is necessary for securing investors, ensuring proper planning, and setting your business up for success. It outlines how you'll turn a profit, stand out in a crowded market, and navigate challenges.
A well-structured business plan is particularly crucial for launching a new business, as it increases the chances of securing funding and achieving success. Investing time upfront can lead to long-term rewards.
How to write a restaurant business plan
To write a restaurant business plan, start with a template tailored for the industry, like our customizable one available for download. Conduct a market analysis to understand your customers and competition.
Utilize restaurant business plan samples as templates to craft a personalized plan that effectively communicates your ideas to potential investors. Explore the key elements of a successful plan below.
What is the most important thing to open a restaurant?
Opening a restaurant is a complex venture, but the most important thing is a clear and solid plan. While passion for food and hospitality is essential, a business plan lays the foundation for everything else.
As a business owner, it helps you define your restaurant concept, target market, financial strategy, and operational details.
How to start a food business with little money?
Six steps to launch a small food company:
1. Choose the category of food products you want to offer.
2. Verify the ideas you have for products.
3. Create a plan for your business.
4. Get to work developing your brand.
5. Establish your web store.
6. Locate and expand your following.
Does a restaurant need a business plan?
Without one, it might be extremely difficult or perhaps impossible to get finance from a bank or investor for your restaurant venture. For this reason, having a business plan is essential. You might find it difficult, if not impossible, to remain in business for very long without the crucial beginning or operating capital.
How many pages can a business plan be?
15 to 20 pages.
A business plan, which is usually 15 to 20 pages long, is a written document that describes your company's operations, goals, and proposed course of action. It outlines the chances you're pursuing, the tools you'll need to reach your objectives, and your definition of success.
How to create a restaurant budget?
To create a restaurant budget, estimate your revenue based on market research and sales forecasts. Calculate fixed costs (e.g., rent, utilities, salaries) and variable costs (e.g., food, beverages). Set aside a contingency fund for unexpected expenses. Regularly review your performance against the budget to make adjustments and keep finances on track.














%20(1).webp?width=200&name=Eat%20(15)%20(1).webp)

-1.png?width=1812&height=1072&name=TripAdvisor%20%26%20More%20Bookings%20(1)-1.png)
-2.png?width=1812&height=1072&name=Google%20Bookings%20(1)-2.png)

-1.jpg?width=200&name=pexels-tidos-mes-3134448-21063847%20(1)-1.jpg)
-1.png?width=200&name=TripAdvisor%20%26%20More%20Bookings%20(1)-1.png)
-2.png?width=200&name=Google%20Bookings%20(1)-2.png)
-1.png?width=200&name=Instagram%20Bookings%20(1)-1.png)
-1-png.webp?width=200&name=Facebook%20Integration%20Rectangle%20(1)-1-png.webp)







.webp?width=200&name=download%20(1).webp)
%20(1)-2.webp?width=200&name=Eat%20(34)%20(1)-2.webp)
%20(1)-2.webp?width=200&name=Eat%20(18)%20(1)-2.webp)









%20(1)-1.webp?width=314&height=175&name=Eat%20(62)%20(1)-1.webp)


.webp?width=144&height=72&name=Eat%20App%20Logo%20(3).webp)